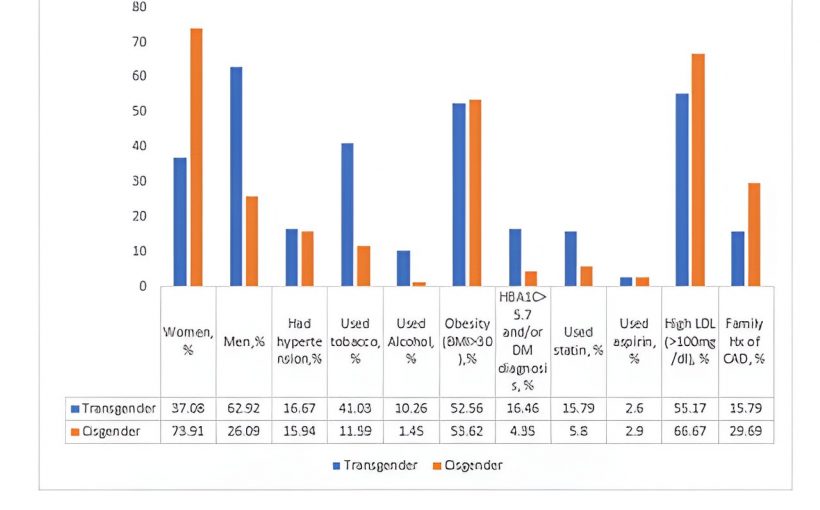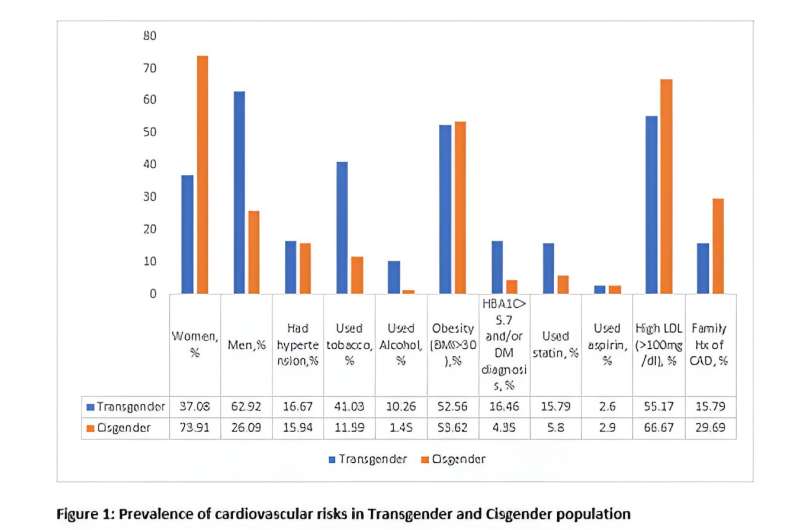
- Participants who identified as transgender were more than six times more likely to use tobacco and almost four times more likely to have prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Those in the trans-male group were 13 times more likely to have obesity (defined by body mass index of at least 30 kg/m2) and nearly 3.5 times more likely to have high cholesterol compared with trans-females. More than 60% of the transgender participants self-identified as trans-males.
- The likelihood of alcohol use, tobacco use and the need for cholesterol-lowering medications was notably increased by 11, 6 and 4 times, respectively, in transgender individuals who received gender-affirming surgery or hormone treatments when compared to other transgender participants, however, the number of people in the study limits the generalization of these findings.
Source: Read Full Article