In a Sounding Board article published in The New England Journal of Medicine, H. Gilbert Welch MD, MPH, Senior Investigator, Center for Surgery and Public Health, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and colleagues present evidence for why they believe that increased diagnostic scrutiny is the primary driver of the rapid rise in melanoma diagnoses.
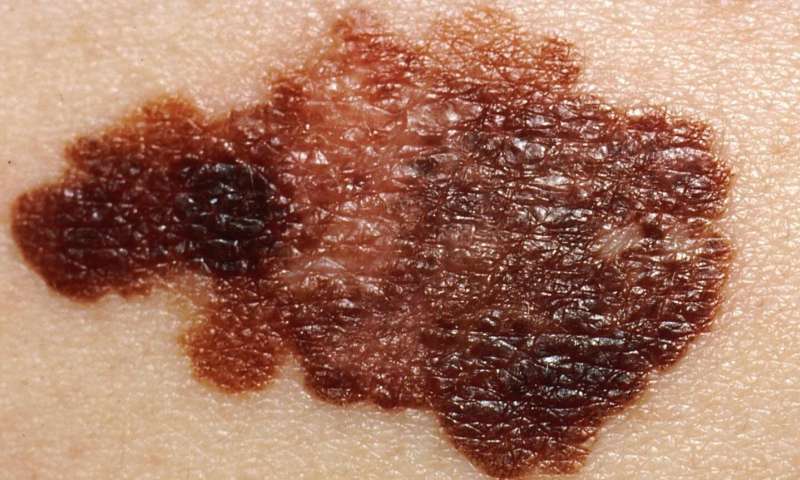
Melanoma of the skin is now the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the U.S. Diagnoses of melanoma are six times as high today as they were 40 years ago. While incidence of melanoma has been rising steeply, melanoma mortality has been generally stable. In a Sounding Board article, Welch and colleagues present evidence for why they believe that increased diagnostic scrutiny is the primary driver of the rapid rise in melanoma diagnoses.
“Melanoma is now the posterchild for overdiagnosis,” said Welch. “Although the conventional response has been to recommend regular skin checks, it is far more likely that more skin checks are the cause of the epidemic—not its solution.”
Among many examples, Welch and co-authors describe a study in which nine dermatopathologists reviewed skin-biopsy specimens used for diagnosis 20 years earlier. Many of the specimens previously diagnosed as benign were now diagnosed as melanoma. Welch and co-authors also share data showing that among the Medicare population, the proportion of beneficiaries biopsied increased every year from 2004 to 2017, nearly doubling over that time. Over the same period, the incidence of melanoma in adults 65 and older also doubled.
The authors point out that there are many potential harms in over-diagnosing melanoma, from the immediate—scarring, wound infection, out-of-pocket costs—to longer term effects such as impeding access to care for people with symptomatic skin diseases.
Source: Read Full Article
