Recently, the teams led by Professor Xuechen Li from Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, The University of Hong Kong (HKU) and Professor Sheng Chen from the Department of Infectious Diseases and Public Health of City University of Hong Kong (CityU), joined hands and made a breakthrough in vaccination development against lethal bacteria Acinetobacter baumannii. Their studies have been published in ACS Central Science.
Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) is a Gram-negative pathogenic bacterium and it causes a wide range of serious infections such as bacteremia, pneumonia, meningitis, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections. Furthermore, A. baumannii tends to acquire resistance to numerous classes of antibiotics via multiple resistance mechanisms and has been identified as an ESKAPE pathogen, a group of pathogens with a high rate of antibiotic resistance. Because of the multi-drug resistant and severe threat to public health, A. baumannii is on the top of the list as the top priority for immediate attentions among the 12 “priority pathogens” requiring urgent antibacterial research and development (R&D) published by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2017.
Researchers worldwide are actively pursuing the development of new antibacterial drugs against multi-drug resistant A. baumannii. Apart from a search for novel antibiotics, vaccination or immunotherapy provides an alternative treatment to protect people from bacterial infections and combat multidrug resistance. Take Glycoconjugate vaccines as an example, it consists of bacteria surface glycans linking to a carrier protein of immunogenicity, have been successfully developed and clinically applied in treatment against bacteria, such as Prevnar 13 as the Pneumococcal vaccine. When people were invaded by the bacteria after vaccination, immune system will recognize the surface glycan and trigger immune response to kill it.
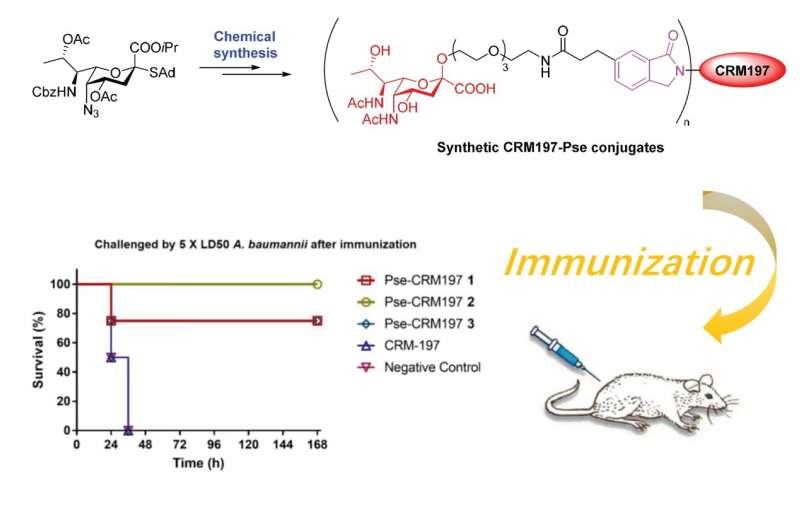
Considering the structural variety and complexity of bacteria surface glycan, difficulty in culturing pathogenic bacteria and possibility of contamination in isolation process, chemical synthesis could be an alternative in obtaining bacteria surface glycan compared with isolation from bacteria. For the past seven years Professor Li’s lab was focusing on the chemical synthesis of pseudaminic acid, a nine-carbon monosaccharide unique to bacteria and commonly present in Gram-negative pathogen surfaces including A. baumannii. His team has developed the highly efficient and stereoselective methods to construct pseudaminic acid-containing glycans. In the current study, Li and Chen’s group chemically synthesized pseudaminic acid-carrier protein conjugate and tested its potential as the anti-bacterial vaccine. They found that anti-pseudaminic acid antibody from vaccinated mice sera reached a high level after vaccination and the vaccinated mice were completely protected from infection of A. baumannii , whereas all control mice received negative control died within 36 hours.
Source: Read Full Article
